CLINICAL STUDIES
Introduction. The standard approach to treating patients with right colon cancer (RCC) is complete mesocolic excision (CME), the main criteria of which include consequent surgical separation by sharp dissection of the visceral fascia layer from the parietal one and high ligation of blood vessels. However, the extent of lymph node dissection is currently not standardized. In European countries, D2 lymph node dissection is more often performed, while in many Asian countries, D3 lymph node dissection, based on the removal of the apical lymph nodes, is widely used. The lack of precise landmarks and insuffcient visualization of the lymphatic system do not allow the surgeon to reliably judge the radicality of the resection of the lymphatic drainage zone without specialized dyes.
The aim of the study was to evaluate the immediate results of regional lymphatic collector mapping in patients with RCC using individual dose calculation of indocyanine green (ICG).
Material and Methods. The study included 63 patients with RCC who underwent laparoscopic right hemicolectomy (LRH) with CME and D3 lymph node dissection between January 2023 and October 2024. All patients underwent colonoscopy with submucosal administration of ICG 1 cm proximal and distal to the tumor on the day before surgery or on the day of surgery at least 3 hours before. In 27 patients (group 1), the ICG dose was determined empirically (0.5–7.5 mg, median 2.0 mg). In 36 patients (group 2), the dose was calculated individually based on the visceral fat area (VFA) determined by abdominal computed tomography (CT). The total ICG dose was 1 mg per 100 cm2 of VFA. All cases were evaluated according to a fve-level scale, with levels 1 and 5 considered as failed mapping and levels 2–4 as a positive result (successful mapping).
Results. Successful mapping was recorded in 22 (81.5 %) of 27 patients in group 1 and in all 36 (100 %) patients in group 2. Moreover, optimal mapping (good visualization of the regional lymph collector in the NIR mode) was obtained in 11 (40.7 %) of 27 and 31 (86.1 %) of 36 patients, respectively (p<0.001). The complication rates were 37.0 % and 19.4 %, respectively (p=0.156), with complications of grade ≥3 according to Clavien–Dindo classifcation in 7.2 % and 2.8 % of patients (p=0.156). During the pathomorphological evaluation of the removed specimen, the median number of examined lymph nodes (LN) was 46 (12–119) and 53 (33–139) (p=0.054), and the median of metastatic LNs was 3 and 4 nodes, respectively (p=0.992).
Conclusion. When mapping the regional lymphatic collector using ICG in RCC, it is advisable to use an individual calculation of the ICG dose based on VFA, which allows achieving the maximum frequency of successful mapping (100 %) and optimal mapping in 86.1 % of cases.
Aim: to evaluate the results of sentinel-lymph-node (SLN) mapping in detecting lymph node metastasis in apparently early-stage ovarian cancer.
Material and Methods. The prospective unicentric study included 48 patients with stage I–IIA ovarian cancer who underwent surgical staging at the Department of Gynecological Oncology of N.N. Blokhin National Medical Research Center of Oncology from 2022 to 2024. Patients were injected with indocyanine green dye into the infundibulo-pelvic and utero-ovarian ligaments (or ligament’s stumps) to map and remove sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs). After the SLNs were identified and removed, pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy was performed.
Results. Of 48 patients, 40 (83.3 %) had successful mapping of at least one SLN. Three patients (7.5 %) had positive nodes: 1 patient (2.5 %) had metaststic para-aortic SLN; 1 patient (2.5 %) had false-negative para-aortic SLN; and 1 patient (2.5 %) had metastatic pelvic lymph node without SLN detection in this region. Thus, the SLN mapping detection rate was 50 % for metastatic lymph nodes in the para-aortic region. None of the patients with detected SLN in the pelvic region had metastatic lymph nodes. No complications related to SLN technique were observed.
Conclusion. The results of this prospective study do not demons trate that lymph nodes status can be fully predicted by SLN evaluation. Further prospective studies are required to evaluate experience of SLN detection in early-stage ovarian cancer.
Background. The majority of breast cancers (BC) are HER2-low defined by an immunohistochemical score of 1+ or 2+ with a negativefluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) test.The prognostic significance of HER2- low BC remains controversial, but demonstrates immunosuppressive activity and disruption of the cGAS- STING pathway. Trastuzumab-deruxtecan is effective in HER2-low due to its immunomodulatory properties. The development of new HER2-targeted therapy is relevant for the correction of the immunosuppressive microenvironment.
Objective: to study the molecular features and clinical significance of HER2-low status depending on the genetic profile of HER2-negative breast cancer.
Material and Methods. A retrospective study (2022–2023) included 282 patients with hereditary and sporadic BC. A genetic analysis of HRR gene mutations was performed at N.N. Petrov National Research Medical Center of Oncology. TILs and pathological response were evaluated. Immunohistochemistry included antibodies to estrogen, progesterone, HER2, Ki67, CD8, CD4, CD68, and CD163 receptors. The statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics v.22.
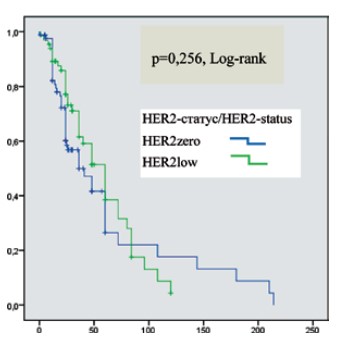
Results. Hereditary BC is often associated with HER2-zero status due to mBRCA1/2 (p<0.001), while mutations in other HRR genes are associated with HER2-low status (p<0.05). HER2-low BC is associated with the luminal A subtype, low tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs 1 score), high proportion of macrophages (CD68≥67 %) and low level of T-lymphocytes (CD4+TILs<2.5 %, CD8+TILs<6 %), which reduces the effectiveness of chemotherapy. With the luminal subtype, HER2-low does not affect diseasefree survival (DFS), but it improves DFS in women under the age of 43 years. The presence of mBRCA2 worsens survival in HER2-zero status, and mBRCA1 in HER2-low breast cancer status. HER2-low status demonstrates discordance between the primary tumor and its metastases, with a common shift from HER2- zero to HER2-low.
Conclusion. HER2-low status is a biomarker in advanced BC that expands therapeutic options. Further development and optimization of breast cancer treatment strategies is required, taking into account the molecular profile and microenvironment of the tumor.
The aim of the study was to evaluate of the efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (nCT) with mFOLFIRINOX regimen for treating patients with resectable pancreatic cancer.
Material and Methods. Since 2020, a prospective phase II clinical trial that tests the effectiveness of mFOLFIRINOX chemotherapy followed by radical surgery compared to surgery followed by chemotherapy has been conducted at Pavlov First Saint Petersburg State Medical University for patients with resectable pancreatic cancer. A preliminary analysis of the immediate treatment outcomes has been presented. As of September 2024, 80 patients were included in the study (standard treatment group: n=41, nCT group: n=39). Patients in the standard treatment group underwent radical surgery followed by mFOLFIRINOX aCT (oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 IV for 120 min, irinotecan 150 mg/m2 IV for 90 min, calcium folinate 400 mg/m2 IV for 120 min, 5-fluorouracil 2400 mg/m2 IV infusion for 46 hours every 2 weeks) for 12 cycles; patients in the experimental treatment group underwent tumor verification at the first stage (endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy with subsequent cytological examination or percutaneous biopsy), after which 6 cycles of mFOLFIRINOX nCT and radical surgery followed by mFOLFIRINOX aCT were performed for 6 cycles. The immediate surgical outcomes, complications and mortality rates were assessed.
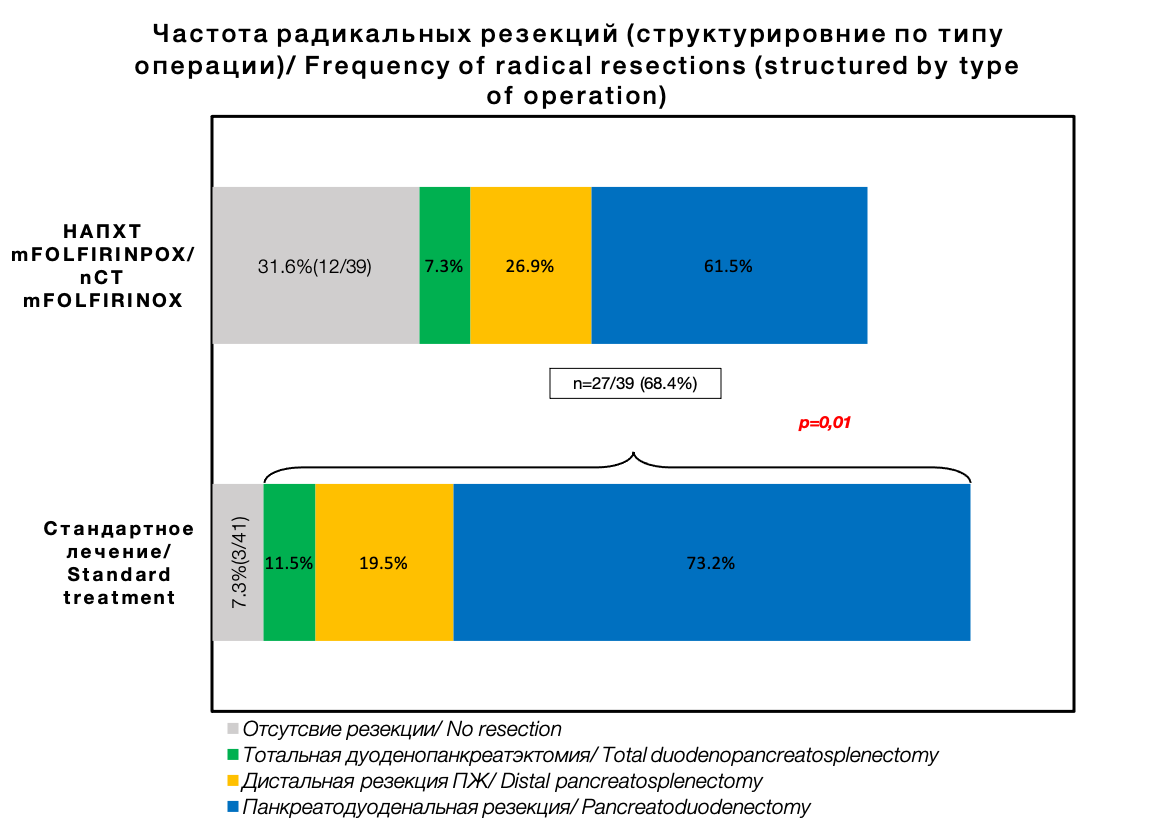
Results. A statistically significant superiority of the nCT group over the standard treatment group was revealed in the following indicators: frequency of portal and/or superior mesenteric vein resections – 10.2 vs 21.9 % (OR 0.44, 95 % CI [0.149–1.329] p=0.04), R0 resections – 88.5 vs 73.2 % (OR 0.6, 95 % CI [0.118–0.909], p=0.03), lymphovascular invasion – 52.6 vs 14.8 % (OR 0.28, 95 % CI [0.108–0.730] p=0.05), microvascular invasion – 55.2 vs 11.1 % (OR 0.26, 95 % CI [0.1–0.669] p=0.01), perineural invasion – 65.7 vs 37 % (OR 0.56, 95 % CI [0.327–0.969] p=0.01), frequency of negative lymph node status (pN0) – 73.1 vs 41.5 % (OR 0.61, 95 % CI [0.331–0.969] p=0.009). Conclusion. nCT is a promising and safe method that can improve immediate treatment outcomes in patients with resectable pancreatic cancer.
Objective: to evaluate surgical treatment outcomes in colorectal cancer patients aged younger and older than 75 years.
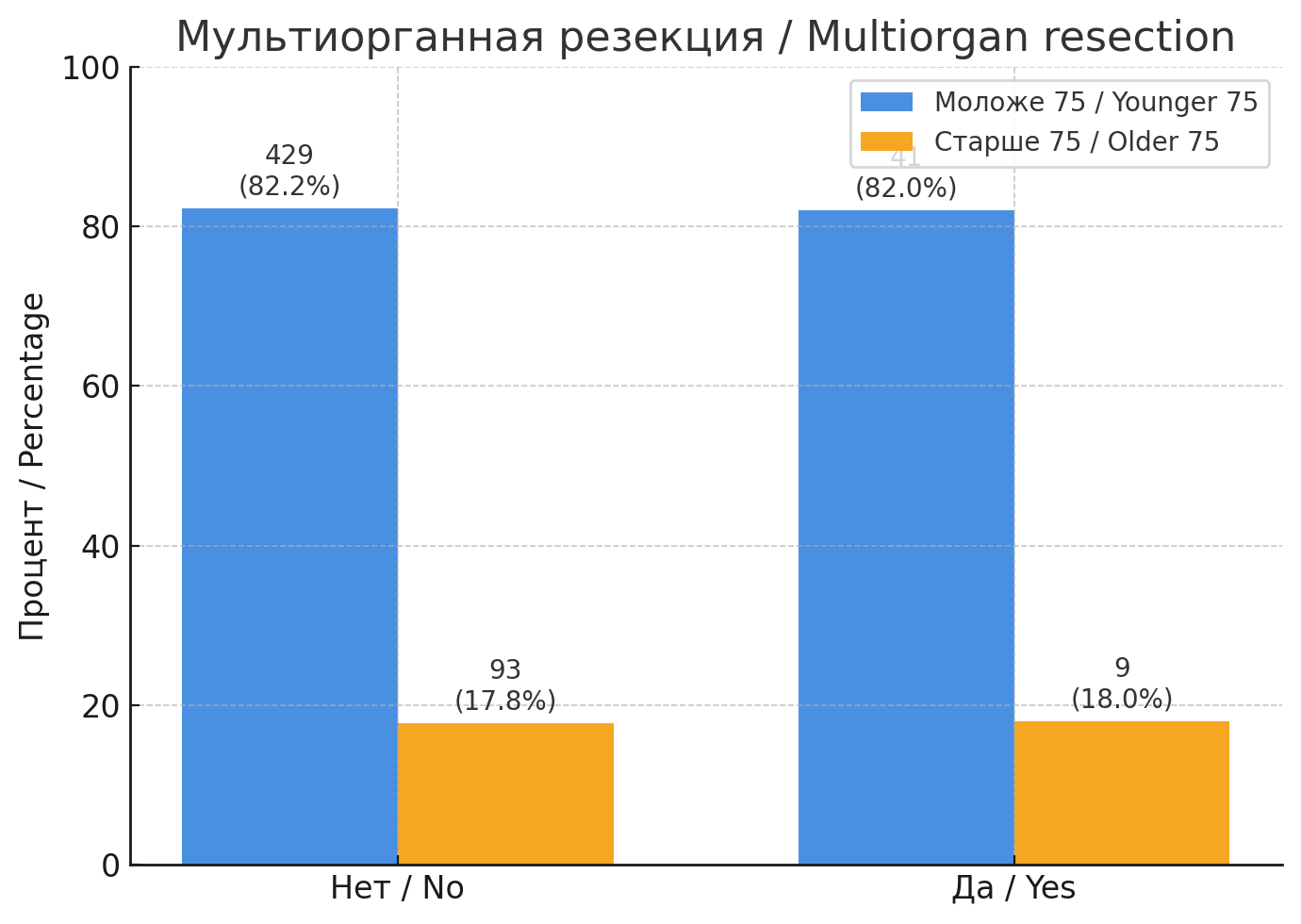
Materials and methods. A retrospective analysis of medical records was conducted for 582 colorectal cancer patients treated between January 1, 2019, and December 1, 2024, at the Department of Abdominal Oncology Surgery, Regional Clinical Oncology Hospital, Ulyanovsk, Russia. Based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, 572 patients were included in the study. Postoperative complications were assessed using the Clavien–Dindo classifcation, and tumors were staged according to the TNM system. The patients were categorized into two age groups: a younger group consisting of patients younger than 75 years, and an older group including those aged 75 years or older.
Results. Univariate analysis revealed no statistically signifcant differences in baseline clinical and demographic characteristics or comorbidities between the patient groups. However, the Charlson comorbidity index was signifcantly higher in patients aged 75 years and older (p < 0.001). Compared to the younger group patients, the older group patients more frequently underwent right-sided hemicolectomy (58, 56.9%), followed by sigmoid colon resection (38, 37.3%). The incidence of anastomotic leakage was higher in older patients than in younger patients, but this difference did not reach statistical signifcance (p = 0.065). No signifcant differences in postoperative complications stratifed by the Clavien–Dindo classifcation were found between the patient groups (p = 0.247). Multilevel logistic regression identifed the following predictors of anastomotic leakage: preoperative albumin level, albumin level on postoperative days 1 and 5, as well as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on postoperative days 1 and 5.
Conclusion. Patient age is not considered an independent factor for anastomotic leakage after colorectal cancer resection. Signifcant predictors of anastomotic leakage include NLR on postoperative days 1 and 5, as well as preoperative albumin levels and albumin levels on postoperative days 1 and 5.
LABORATORY AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES
Background. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are now widely used for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and disease progression is often linked with the development of resistance to these drugs. There is a need for additional theranostic tools, and they may include expression levels of certain microRNAs (miR).
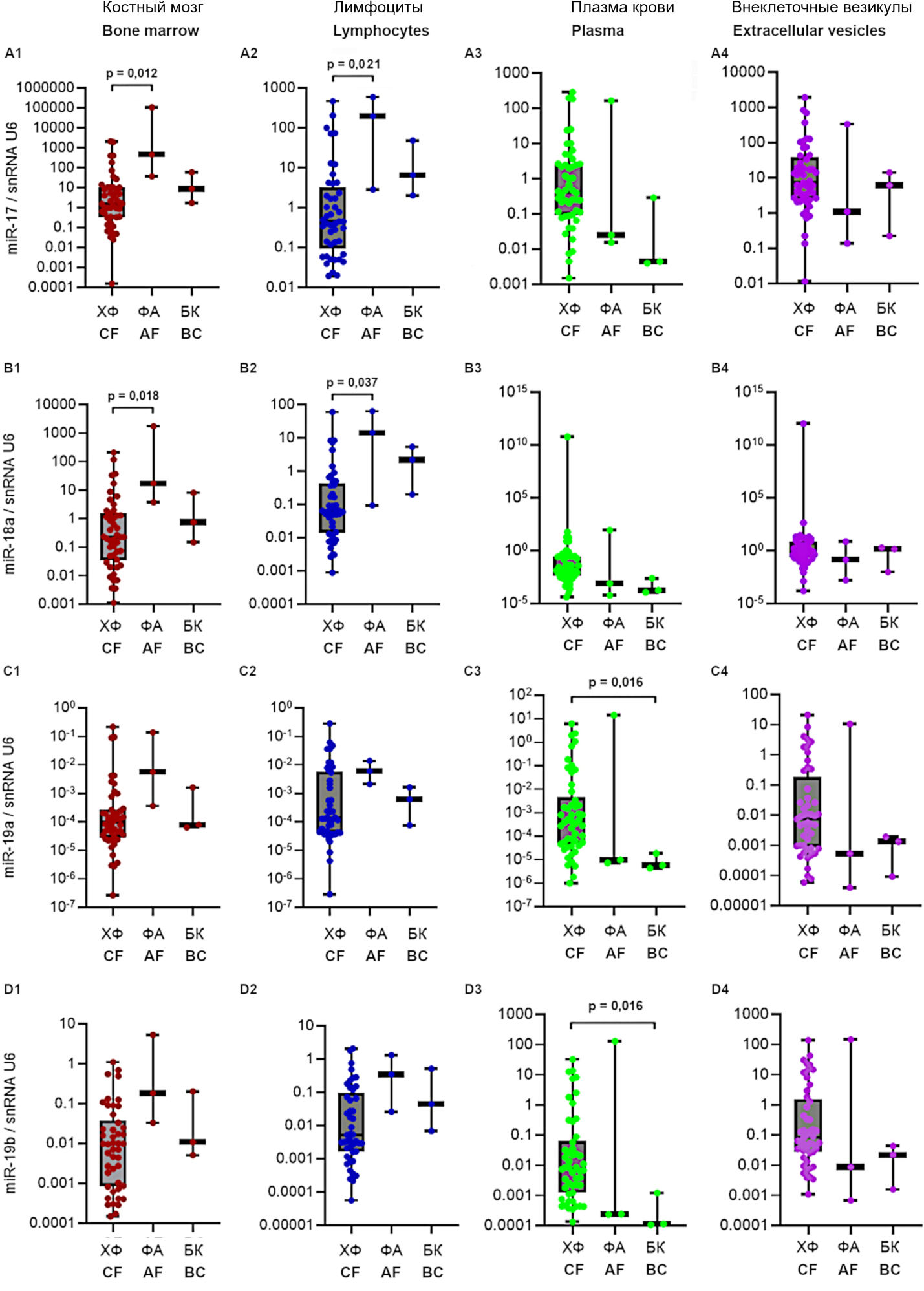
Purpose: to study expression levels of miR-203a and of miR-17-92 cluster members in bone marrow and peripheral-blood components (lymphocytes, plasma, and extracellular vesicles) from CML patients with various clinical characteristics and treatment responses.
Material and Methods. Blood and bone marrow samples were collected from 56 patients having a CML diagnosis from the City Hematology Center at the government-funded healthcare institution (Novosibirsk Oblast) City Clinical Hospital No. 2 from the years 2016 to 2017. Expression levels of miRNAs were quantifed by reverse-transcription real-time PCR according to the TaqMan principle.
Results. In bone marrow and blood lymphocytes, expression levels of miR-17, miR-18а, and miR-20a were higher in patients in the acceleration phase (FA) as compared to the chronic phase (CF) and in patients with an unfavorable prognosis. In plasma, expression levels of miR-19a and miR-19b were higher in patients with CF compared to the blast crisis (BC) phase and higher in patients with a favorable prognosis. MiR-19a expression was also higher in extracellular vesicles of patients with a favorable prognosis, and miR-203 expression was higher in patients with a favorable prognosis in extracellular vesicles and in blood plasma. Furthermore, miR-203 expression proved to be signifcantly greater in extracellular vesicles of patients who achieved a major molecular response.
Conclusion. MiR-17, miR-18а, and miR-20a in bone marrow and lymphocytes seem to be the most promising for the possible practical application, and the same is true for miR-19a and miR-19b in blood plasma and miR-203 in blood plasma and extracellular vesicles.
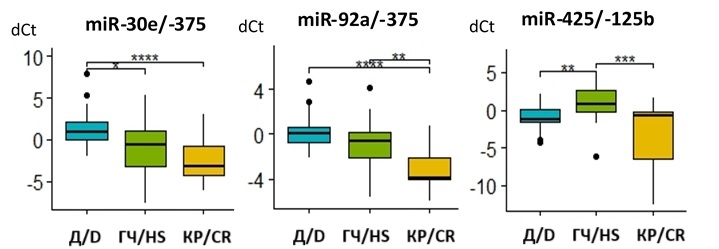
Background. Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is a highly aggressive and challenging-to-treat cancer. the search for markers to predict early CRPC for timely treatment adjustments and further study of these markers as potential targets for new CRPC therapies is a crucial task in modern molecular biology and medicine. extracellular miRnas show promise as diagnostic and prognostic markers for prostate cancer (PC) and particular for CRPC.
Aim of the study: a comparative analysis of the expression of 14 miRnas in the urine supernatant of patients with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (HsPC), CRPC, and donors (D).
Material and Methods. the analysis was conducted using the real-time qPCR. a pairwise normalization method was used to search for diagnostic miRna expression signatures.
Results. twenty-nine differentially expressed pairs of miRnas were identified. In this case, miRna-375 was included in the largest number (n=7) of diagnostically significant pairs. three miRna pairs (miRna-144/222; 205/375; 222/125) showed the highest sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing CRPC when using both HsPC patients alone and the combined group of donors and HsPC patients as the control group.
Conclusion. the results obtained indicate that the assessment of the relative expression of urinary extracellular miRnas has a significant potential for diagnosing highly aggressive castration-resistant prostate cancer.
ONCOLOGY PRACTICE
Background. External beam radiation therapy (eBRt) is one of the primary treatment modalities for patients with prostate cancer. Despite advancements in radiotherapy technology and planning, significant challenges in managing radiation-induced reactions remain. In this regard, the search and development of new drugs to mitigate side effects from radiotherapy is a critical research area.
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effect of synbiotics (VedaBiotic, Phytolysate Gastro, Phytolysate and urological) on the development of radiation-induced bladder and bowel reactions, as well as to study the state of gut microbiota during eBRt in prostate cancer patients.
Material and Methods. The study included 15 patients diagnosed with stage t3–4n0M0 prostate cancer (adenocarcinoma) receiving eBRt at Radiotherapy Department of novosibirsk Regional Clinical Oncology Center. From november 2024 to December 2024, patients received 3D conformal radiation therapy delivered to the prostate, seminal vesicles, and pelvic lymph nodes at single doses of 2.5/2.5/1.8 Gy to total doses of 80/80/50 Gy in 28 fractions, respectively. Patients used synbiotics as the dietary supplement during radiation therapy in accordance with the instructions on the label. all patients underwent maximum androgen blockade including chemical castration with lHRH agonists.
Results. A survey of patients showed reduction in nocturia to 2–3 episodes per night. there was also a decrease in urination discomfort and the absence of symptoms of flatulence. PCR analysis detected an increase in beneficial bacteria, namely lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species (lacto-bifidobacteria), and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, indicating a restoration of a healthy balance in the intestinal microflora.
Conclusion. the results obtained show that the inclusion of synbiotics (VedaBiotic, Phytolysate Gastro, Phytolysate and urological) in the diet can reduce dysuric symptoms, flatulence, and help restore intestinal microflora balance in patients receiving eBRt to the prostate, seminal vesicles, and pelvic lymph nodes.
REVIEWS
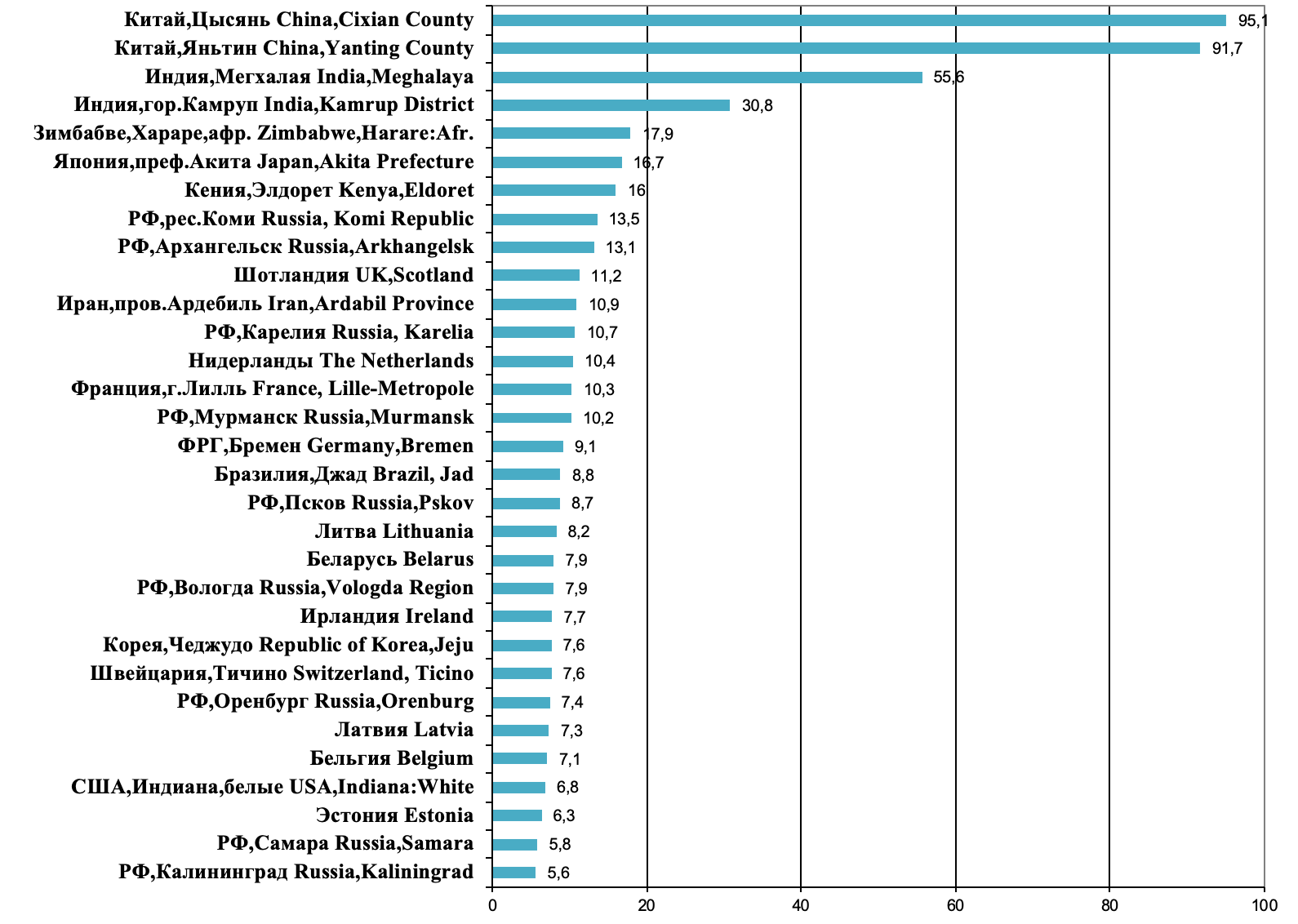
The aim of the study is to analyze incidence and mortality of esophageal cancer (EC) in the world and Russia; conduct a systematic review of literature of eC causes.
Material and Methods. GlOBOCAN, Cancer Incidence in Five Continents and the annual Directories of Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Russia (MNIOI P.A. Hertsen) were used; a systematic search of the published papers on EC risk factors was carried out in the PubMed and Cochrane library databases.
Results. EC is characterized by pronounced geographic variability in incidence. High incidence is noted in China, Mongolia, Iran. In Russia incidence of EC is low. In some regions, however, incidence is twice as high as in Russia overall. In the world, 85 % of EC cases have the histological structure of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and 14 % – adenocarcinoma (AC). SCC is more common in the countries of east, south and Central Asia, AC prevails in countries of north america, Western and northern europe. the incidence of SCC is decreasing, while incidence of aC is increasing. The main risk factors for SCC are smoking, consumption of alcohol, hot tea, opium, exposure to indoor biomass (wood) smoke, and dietary deficiency in vitamins and minerals. The main risk factor for AK is overweight. The risk of AC is increased in people with Gastro–eesophageal Reflux (GER) and Barrettes esophagus (BE). Molecular signatures caused by EC risk factors have been identified, including mutations, associated with tobacco smoking, alcohol consumption and opium use. Mutations caused by enzymes of the APOBEC family have also been discovered. Preventive measures aimed at reducing the prevalence of SCC risk factors, in particular, control of tobacco smoking, consumption of alcohol, diet modification have already led to a decrease in the incidence of EC. However, there remains a need to continue active preventive work, taking into account regional patterns. Prevention of AK, which should include control of excess weight, timely diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux GER and BE, is not yet very effective.
Conclusion. The described risk factors and associated mutational signatures do not explain the pronounced geographic variability in EC incidence. Further studies are needed to search for unknown carcinogenic factors with a non-mutational, but epigenetic mechanism of action.
Objective: to systematically analyze the data available in the modern literature on sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer in various clinical situations.
Material and Methods. The search was conducted in the Web of science, PubMed, scopus, Google scholar databases. A total of 213 sources devoted to sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer were analyzed, of which 48 were included in the review.
Results. Sentinel lymph node biopsy has been established as a standard procedure in early stages of breast cancer, demonstrating efficacy and safety in small tumors, intact lymph nodes and micrometastases. Currently, there is a clear trend toward expanding sentinel lymph node biopsy indications into more complex cases, including changes in lymph node status after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, multicentric cancer, and recurrent breast cancer. Studies are underway to evaluate the safety of sentinel lymph node biopsy during pregnancy, opening up new perspectives for the treatment of this vulnerable group of patients. Expanding the indications for sentinel lymph node biopsy will help avoid radical lymphadenectomy and its associated complications, such as postmastectomy syndrome. this, in turn, will significantly improve the quality of life of cancer patients by reducing postoperative morbidity and accelerating rehabilitation.
Conclusion. Further study and implementation of expanded indications for sentinel lymph node biopsy is a promising direction in modern oncology aimed at optimizing treatment and maintaining the quality of life of patients.
Objective. Numerous genetic alterations that are currently incurable are the cause of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), including clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). studying the genetic profile of ccRCC and biomolecules involved in the execution of genetic modifications is pertinent because of this fact, as it may serve as the foundation for the creation of targeted therapeutic approaches. The aim of the study was to analyze and summarize the most recent scientific literature outlining contemporary therapy options for RCC treatment as well as the causes of the low efficacy of biological treatment methods.
Material and Methods. Key words and phrases such as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), molecular biomarkers and clear cell renal cell carcinoma, multi-omic profiling and renal cell carcinoma, signaling pathway and renal cell carcinoma, stem cell subtypes and clear cell renal cell carcinoma, treatment strategies and renal cell carcinoma were searched for and analyzed in PubMed and elibrary.ru databases from 2020 to 2025. We used reviews and original research, primarily from 2020 to 2025, as the primary reference sources for each theme area, while papers with redundant or excessively overlapping content were disregarded. From 2020 to 2025, we chose 79 pertinent works by both domestic and foreign authors.
Results. The VHl and BaP1 suppressor genes are the most extensively researched genetic alterations in RCC, including ccRCC. In addition to the utilization of critical immunological points and different tyrosine kinase inhibitors, the search for new points (genes, signaling molecules, and proteins) as possible solutions for novel treatment approaches is still ongoing.
Conclusion. Genomic abnormalities are considered to have an important role in the pathophysiology of RCCs, particularly ccRCC. The effectiveness of biological treatment methods based on retrospective studies, the influence of the tumor's immune microenvironment, and the expression of molecules on the tumor cell surface that can decrease the effectiveness of medications must all be taken into consideration when selecting a therapeutic approach for patients with RCCs.
Purpose of the study: to conduct a systemic literature review regarding current diagnosis and treatment strategies for ewing sarcoma (ES).
Material and Methods. The search for material for the review was conducted in the Medline, Web of science and Russian science Citation Index libraries. a total of 352 sources published during the period from 2004 to 2024 were selected for the analysis. The review was based on 67 publications.
Results. While surgery and radiation therapy have been crucial in treating ES, the introduction of chemotherapy has significantly improved patient outcomes. Many effective multidrug chemotherapy regimens developed in the 1960s and 1970s are still used as induction therapy for ES patients today. Much attention is paid to the problem of treating patients with relapses and refractory disease that are poorly responsive to chemotherapy. Currently, studies are underway to assess the feasibility of combining cytostatics with tyrosine kinase inhibitors, Dna repair inhibitors, inhibitors of other molecules, and autologous vaccines. available data regarding the effectiveness of high-dose chemotherapy with autologous transplantation and CaR-t cell therapy are contradictory. an obstacle to getting relatively rapid results from these studies is the small number of patients, which dictates the need for multi-center patient recruitment. In addition, the increased requirements of state regulatory bodies due to the childhood and adolescence of a large proportion of patients leave their mark.
Conclusion. Despite significant advances in the treatment of primary localized ewing sarcoma, the treatment results of metastatic disease and relapses are far from satisfactory. While the possibilities of cytostatic therapy appear to be exhausted, molecular targeting drugs have not yet received convincing evidence of clinical significance. However, future advances in treatment should still be expected from drugs that target the key points of the ES oncogenesis.
Objective. This review aimed to study the role of immune proteasomes in the mechanisms of lymphatic metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer (nsClC).
Material and Methods. The review’s literature search was conducted using the Medline, Cochrane library, and elibrary databases, with a focus on publications from the last decade.
Results. The concepts of molecular mechanisms of lymphatic metastasis in lung cancer, including the role of immune proteasomes in the development of nsClC were presented. Studies indicating the involvement of proteasomes in the regulation of angiogenesis and cell locomotion processes were found. An increase in the expression of the PSMB8 and PSMB9 genes encoding immunoproteasome subunits in nsClC cell cultures was described. Information that immunoproteasomes could be a therapeutic target in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer was presented.
Conclusion. The study of the mechanisms of lymphatic metastasis in cancer development remains crucial in cancer research. The data obtained have shown that proteasomes are a promising molecular target and their further study can open new horizons in the fight against cancer.
CASE REPORTS
Background. Paragangliomas are rare neuroendocrine tumors that often located paravertebrally in the retroperitoneal space and near major abdominal blood vessels. Surgical resection is the primary treatment for paragangliomas. A close adjacency between a tumor and the main vessels requires a combined treatment approach: a surgical resection of a tumor along with a portion of the vascular trunk, ensuring that the removed tissue is within the healthy surrounding areas. Separation of the tumor from the vessel may potentially leave a microscopic margin of tumor cells on the vessel wall (R1 resection) and usually results in damage to the vessel and significant blood loss.
Case presentation. We present here the case of surgical treatment of paraganglioma of the organ of Zuckerkandl in a 52-year-old female patient. A close adjacency of the tumor to the aortic bifurcation required tumor resection involving the aortic bifurcation and subsequent reconstruction of the main blood flow using a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PtFe) bifurcation aorto-common iliac alloprosthetic graft (PtFe conduit). The postoperative period was uneventful. The patient is stable and is currently under follow-up care.
Conclusion. This case report demonstrates the feasibility of performing radical surgery in patients with retroperitoneal paragangliomas closely adjacent to the major vessels.
Background. Epidemiological studies show that the incidence of synchronous multiple primary malignant neoplasms ranges from 2 % to 17 %. the co-occurrence of lung cancer and lymphoma accounts for 15 % of all combinations of lymphoproliferative diseases with malignant neoplasms of other organs. Currently, there is no universally accepted diagnostic and treatment strategy for this patient group.
Objective: To present a series of clinical cases demonstrating the significance of a personalized approach in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with the concurrent diagnosis of lung cancer and lymphoproliferative diseases.
Case reports. We report two cases of synchronous lung cancer and B-cell lymphoma. In both cases, diagnosis of multiple primary malignancies guided optimal treatment strategies.
Conclusion. Lung cancer should be included in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary lesions in patients with chronic leukemia or lymphoma. a thorough examination and morphological verification of the identified changes in this group of patients will help to choose the correct treatment strategy.
Currently, the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab is recommended for first-line therapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The accumulated world experience of using this treatment modality allows us to state that it significantly improves the overall prognosis of the disease.
The aim of the study was to evaluate the feasibility of using the combination of atezolizumab + bevacizumab as a conversion therapy for HCC. Case presentation. We report a case of conversion therapy for initially unresectable right-lobe HCC. Due to the insufficient volume of the remaining liver parenchyma (less than 25 %), right-sided hemihepatectomy was considered inappropriate. At the initial stage of treatment, 20 courses of conversion therapy with the atezolizumab + bevacizumab regimen were administered, which was accompanied by a minimum number of adverse events. Subsequently, taking into account the partial response of the tumor to antitumor therapy, radical surgery involving the resection of liver segment s7–8 was performed. Histological examination of the surgical specimen revealed a complete pathological response.
Conclusion. This case report demonstrates the efficacy of atezolizumab + bevacizumab combination as a conversion therapy for HCC, resulting in complete pathological response. The experience gained emphasizes the need for further research in this area.
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) of the female reproductive system, including the cervix, are considered to be extremely rare localizations. the majority (about 80 %) of these cervical NETs are small-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas (SCNECs), which are highly aggressive and have a poor prognosis. Many SCNECs are not recognized leading to a missed diagnosis. Diagnosis relies on identifying neuroendocrine differentiation through immunohistochemical (IHC) examinations, but sometimes this step is omitted.
Case presentation. We herein report a case of a low-differentiated large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix in a 40-yearold woman. Verification of the diagnosis was challenging, that required the use of an extended diagnostic complex to identify the optimal management strategy. After surgery the patient received a total of 4 lines of chemotherapy and underwent IHC testings. However, despite all efforts, the patient’s condition worsened significantly, leading to the death 2 years and 1 month after her initial visit.
Conclusion. Vague symptoms, aggressive progression, diagnostic difficulty, and limited treatments indicate the need to create specialized centers for the treatment of NETs of any tumor grade and location.
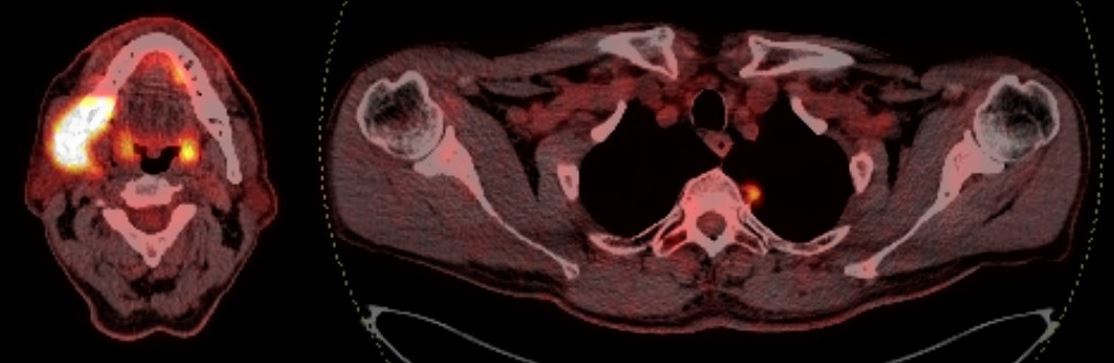
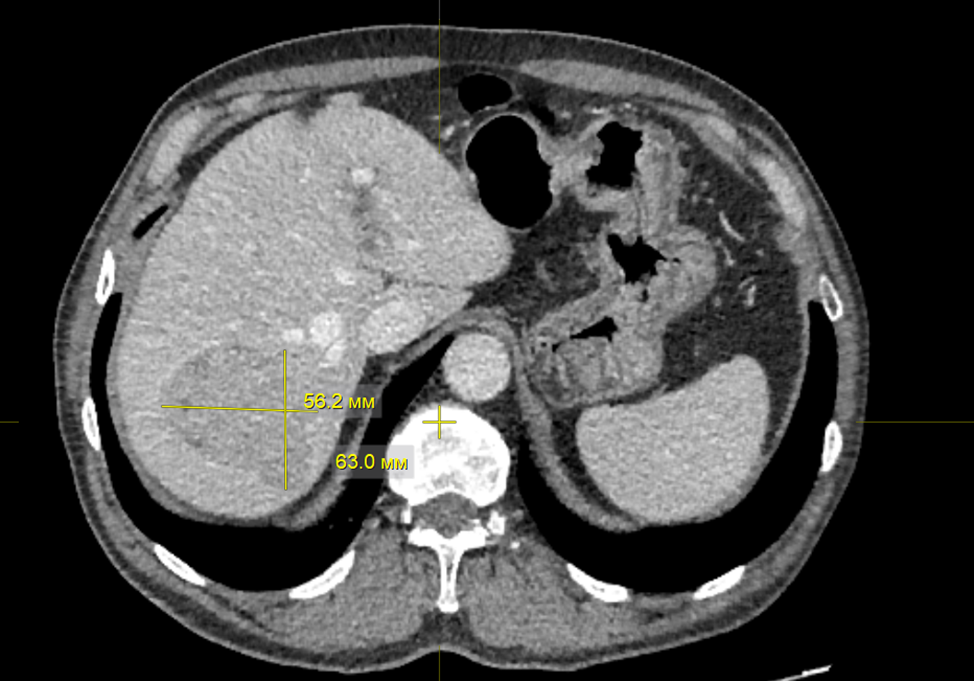
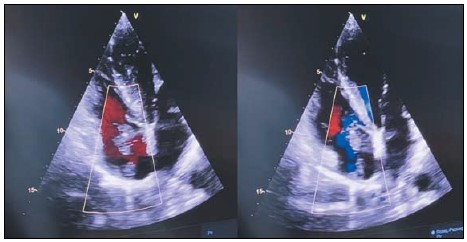
Background. Ovarian carcinoid tumors are rare, representing about 0.1 % among all ovarian tumors and 0.8 to 5 % of carcinoid tumors. Strumal carcinoid is a rare type of ovarian teratoma composed of normal thyroid tissue (struma) and a carcinoid (neuroendocrine) tumor. While most cases are benign, some may exhibit malignant features, prompting treatment as a low-potential malignancy.
Description of the clinical case. We report a case of giant ovarian strumal carcinoid with distant metastasis in the right atrium presenting as a free-floating thrombus. The patient underwent two-stage radical surgery.
Conclusion. This case report demonstrates the importance of comprehensive preoperative clinical diagnosis, intraoperative assessment and histopathological diagnosis. With this pathology, which is often asymptomatic, various diagnostic examinations have low specificity and sensitivity, and in most cases the diagnosis is based on the results of a postoperative histology examination.
ANNIVERSANES
ISSN 2312-3168 (Online)